On September 24, 2024, our expert Irina Barac, Junior Consultant at BEO BERLIN, gave a keynote speech on biocompatibility along the product life cycle. The lecture took place as part of the Treffpunkt Medizintechnik. The Treffpunkt Medizintechnik brings together experts from the medical device industry and offers a platform for the exchange of expert knowledge and innovative strength. We were particularly pleased about the commitment and expertise of our junior consultant and, of course, about the market of ideas at this event.
To further share Irina's insights and to inform you, dear reader, we have summarized the contents of Irina’s keynote here., zu informieren, haben wir den Inhalt des Vortrags hier für Sie zusammengefasst.
What is biocompatibility?
At the beginning of the keynote stands the explanation of the term biocompatibility. The legal definition according to EN ISO 10993-1 defines biocompatibility as the ability of a medical device or material to perform with an appropriate host response in a specific application. Irina explained to us what is meant by these complicated words: a product is biocompatible if and only if it is well tolerated by living organisms and has no negative effects on the body.
EN ISO 10993-1 is particularly important because it provides methods and guidelines for meeting the requirements of the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). This EU-regulation, which has been in effect since 2017, requires that compatibility between the materials of a medical device and the biological tissue of the user must be ensured. Not only are manufacturers legally obliged to prove the biocompatibility of their products, but they are also liable for possible incidents that can be traced back to a lack of biocompatibility.
Biocompatibility and the product life cycle
A key topic of the presentation is how to ensure biocompatibility throughout the entire product life cycle of a medical device. Irina emphasizes that biocompatibility is not only important during the development of a product, but must be continuously monitored throughout its entire life cycle. This begins with the planning of the product and extends through its market launch and the constant monitoring of the product on the market.
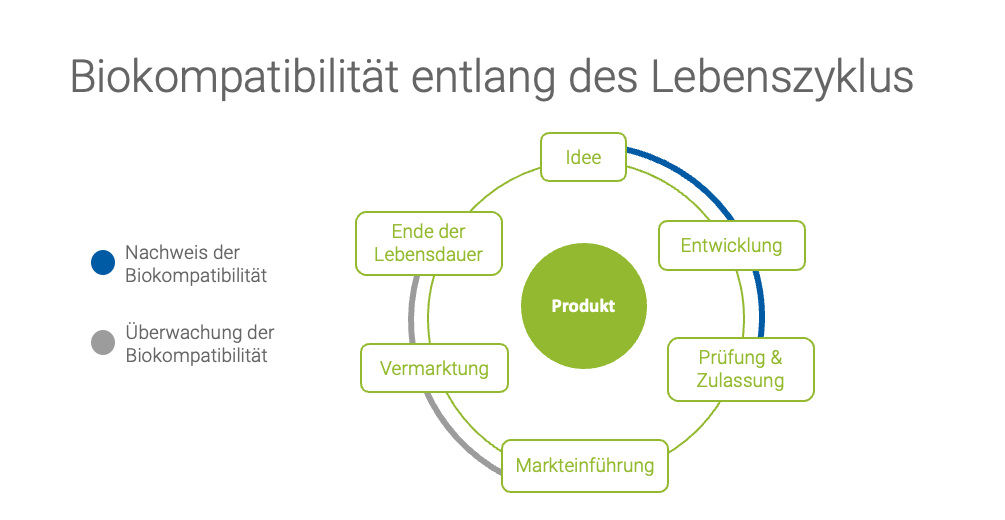
In the planning phase of a new medical device, biocompatibility should be considered early on to ensure that the materials used meet the requirements. During the conformity assessment procedure, biocompatibility is documented in the technical documentation. . Even after market launch, biocompatibility must be regularly reviewed to ensure that the product does not cause any unwanted biological reactions.
Proving biocompatibility: A guide
In the rest of her presentation, Irina presents a guideline for the verification process of biocompatibility. This process begins with characterizing the materials used. This includes not only the material itself, but also factors such as additives, residues, potentially leachable components, and the material's physical properties. External factors such as the manufacturing process, packaging, cleaning and sterilization, and product aging can also influence biocompatibility.
After reviewing all relevant material data, the manufacturer decides whether these are sufficient to rule out a biological risk. In some cases, additional biological testing may not be necessary if an equivalent, marketed product already exists or sufficient data is available in the literature or from suppliers. However, if this is not the case, EN ISO 10993-1 provides guidance on determining which biological tests are necessary.

Biological testing and contact categories
One determining factor in establishing the biological endpoints is the type and duration of the medical device's contact with the body. Irina explains that there are three categories of contact:
- Body surface contact:: This includes products that come into contact with intact skin, mucous membranes or broken skin.
- Body interior: This includes products that come into indirect or direct contact with blood circulation, tissue, bones or organs.
- Implants: This category includes products that remain in the body permanently and are in direct contact with tissue or blood.
In addition to the type of contact, the duration of contact is divided into three categories: limited exposure (up to 24 hours), prolonged exposure (24 hours to 30 days) and long-term exposure (over 30 days). The cumulative contact duration is particularly important here if a product is used multiple times.
On the basis of these factors, a decision is made as to which biological endpoints need to be tested to demonstrate biocompatibility. After thorough discussion, certain endpoints may be excluded from the test in some cases. Standard EN ISO 10993-1 provides a complex matrix to help determine which tests are necessary.
Continuous monitoring and re-evaluation
Demonstrating biocompatibility is not a one-time task. Irina emphasizes the importance of continuously monitoring medical devices, especially after they have been launched. Manufacturers must collect incidents and trends and regularly conduct literature reviews to ensure that nothing new has been published that could cast doubt on the biocompatibility of the product. If any changes are made to the product, such as a change in material or manufacturing methods, biocompatibility must be re-evaluated.
Conclusion
Irina concludes that the goal of biocompatibility assessment is to ensure that medical devices that come into contact with the human body do not pose any biological hazards to patients or users. EN ISO 10993-1 gives clear guidance on the steps necessary to provide this evidence. Biocompatibility must not only be taken into account during product development, but also monitored throughout the entire life cycle of a product. This is the only way to ensure that legal requirements are met and that patient safety is sufficiently guaranteed.

(1 Rating(s), average: 5.00 out of 5)
Loading...

